National policies are tools that stimulate the growth and development of a country. Indeed, national policies are potent instruments wielded by governments to navigate the complexities of economic growth and development.
Through strategic policymaking, governments can influence various facets of society and the economy, fostering conditions conducive to progress and prosperity. Moreover, national policies serve as guiding frameworks that align the collective efforts of government agencies, businesses, civil society organisations, and individuals towards common goals.
They provide the necessary direction and incentives for stakeholders to collaborate effectively, channel resources efficiently, and drive sustainable development initiatives forward. Nepal faces several complex and interrelated challenges that are affecting its social, political, and economic development.
These challenges often overlap and reinforce each other, creating a complex web that impedes the country’s overall progress.
Challenges
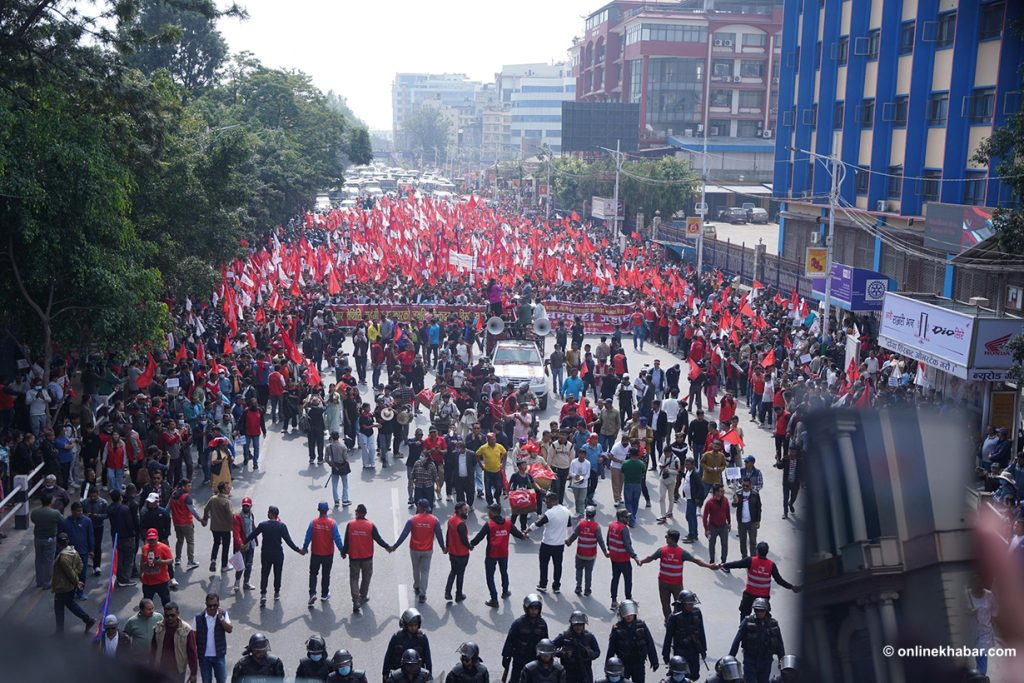
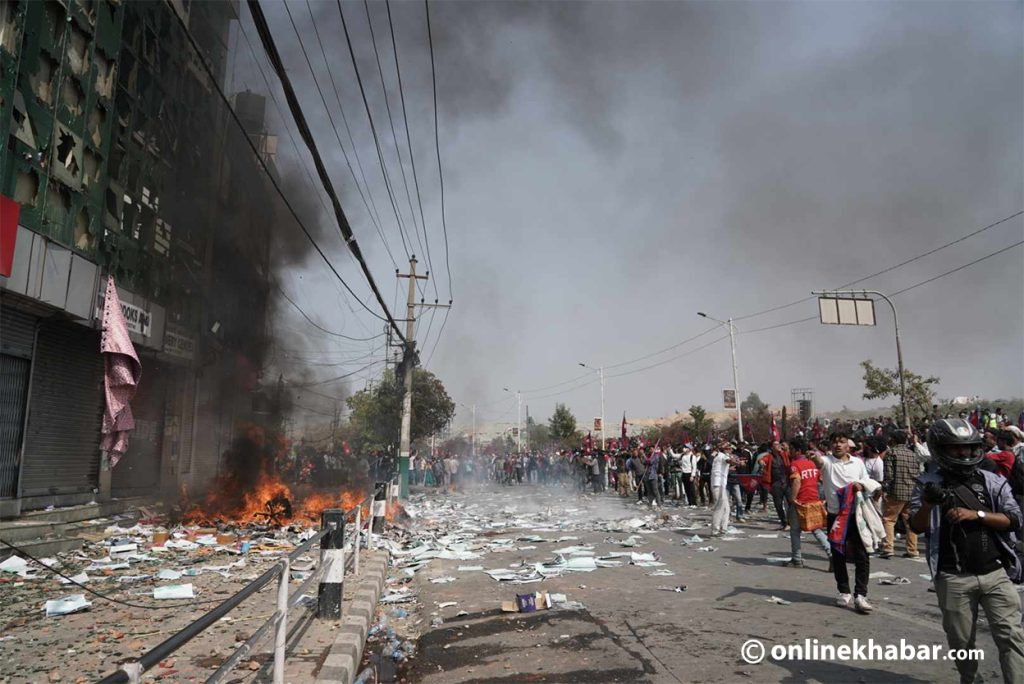
One major policy issue facing Nepal is the need for effective governance and institutional reform. Nepal has been grappling with political instability and governance challenges for many years, which have hindered the implementation of policies and reforms, and this has negatively impacted its development.
There have been numerous changes in government, frequent elections, and an absence of strong and stable leadership. This has resulted in a lack of progress on key issues such as economic development, poverty reduction, and infrastructure improvement. Corruption, lack of accountability, and inefficiency in public service delivery remain persistent problems. Additionally, socioeconomic issues such as poverty, inequality, and access to basic services like education and healthcare continue to be pressing concerns for Nepal.
The contemporary policy issue of Nepal is related to federalism and decentralisation. Since the adoption of a new constitution in 2015, Nepal has been transitioning into a federal system, dividing the country into seven provinces.
There is a struggle to implement a new constitution that satisfies all ethnic and political groups. However, there have been ongoing debates and challenges regarding the implementation of federalism, including issues related to resource allocation, power-sharing between the federal government and provincial governments, local governments, and the restructuring of administrative mechanisms.
The successful implementation of federalism remains a significant policy challenge in Nepal, requiring careful coordination, dialogue, and institutional capacity building at all levels of government.
The key aspect of this issue is the ongoing debate over the division of powers between the federal, provincial, and local levels of government.
Conflicts
There have been disagreements and conflicts between different tiers of government regarding their respective roles and responsibilities. Additionally, some provinces have raised concerns about inadequate resources and autonomy, leading to tensions between the central government and provincial administrations. Key issues include the delineation of provincial boundaries, distribution of fiscal resources, and allocation of authority between different tiers of government.
Disputes have arisen between the federal government and provincial governments over jurisdictional matters, leading to political tensions and delays in the implementation of key policies and programs.
Another related issue is the need for effective governance and capacity building at the provincial and local levels.
Many provinces and local governments have struggled with limited resources, lack of expertise, and bureaucratic inefficiencies, hampering their ability to deliver essential services and implement development projects effectively. And next significant policy issue in Nepal is economic development and poverty reduction. Despite making progress in reducing poverty over the years, Nepal remains one of the poorest countries in South Asia, with significant disparities between urban and rural areas. Economic growth has been hindered by factors such as political instability, corruption, inadequate infrastructure, and reliance on remittances.
Furthermore, issues such as corruption, economic development, infrastructure improvement, social inequality, and environmental degradation remain significant challenges for policymakers in Nepal. Efforts to promote sustainable development, improve infrastructure, and attract investment are key priorities for the Nepalese government. Addressing social issues such as gender inequality, access to education and healthcare, and environmental sustainability is critical for the country’s long-term development.
Additionally, ensuring participatory decision-making processes and incorporating the voices of marginalized communities are crucial for designing effective policies and programs that meet the needs of all Nepalese citizens.
In conclusion, addressing the multifaceted policy challenges in Nepal demands a united front involving government institutions, civil society organizations, the private sector, and international partners. By fostering collaboration and synergy among these stakeholders, Nepal can navigate its complex issues more effectively. Key to success will be the development and implementation of robust policies, supported by comprehensive monitoring mechanisms to ensure accountability and progress. Through this concerted effort, Nepal can pave the way towards sustainable development, fostering prosperity and well-being for its people now and in the future.