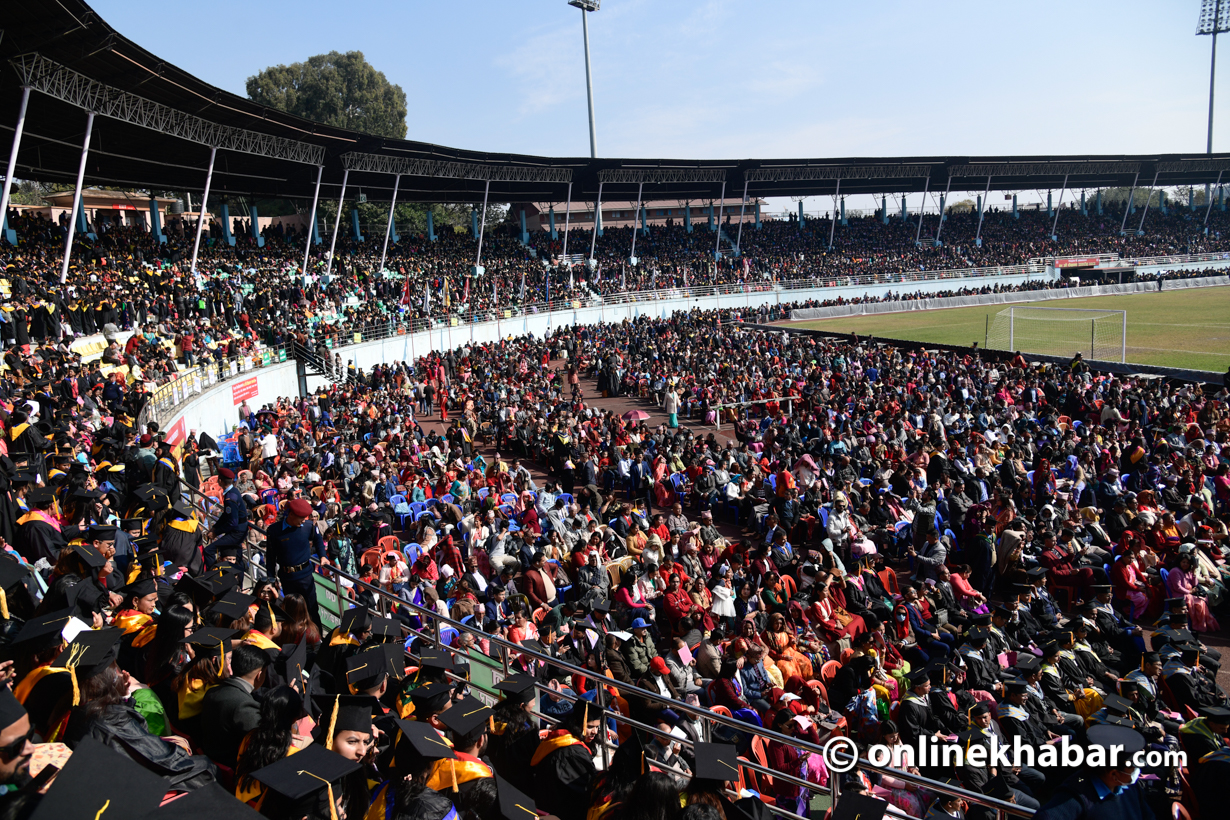
Just last year, Nepal witnessed three national elections in a row—to elect local, provincial and federal legislative and executive bodies. While national politics is all centred on the presidential election to be held next week, there is some other election that a significant size of the country’s youth is thinking of now: the FSU elections.
Tribhuvan University, the oldest and biggest university in Nepal, has announced to hold the elections of free student unions (FSUs) at its constituent and affiliated colleges on March 19.
So what are these FSU elections all about? Onlinekhar explains here.
What are these FSUs?

The history of FSU as an institution dates back to 1960. Student unions came into existence as resistance to the late King Mahendra Shah’s autocratic Panchayat system he began after dissolving the first democratically elected parliament and taking control of executive powers.
The situation created a space for student politics at the old university, which consequently resulted in the elections. The first FSU elections were held in 1962.
The FSU is also known as the hub for potential leaders who can lead the country in the future. There are many top-notch politicians in the current Nepali political scenario who got a rise from the FSU, such as Sher Bahadur Deuba, Gagan Thapa, Ram Kumari Jhakri, Shankar Pokhrel and Yogesh Bhattarai to name a few.
The FSU elections will be held among student leaders of the colleges affiliated with the TU. The candidates are basically the representatives of the student unions affiliated with major political parties. The voters include the students who have officially enrolled at the institution.
The election at each college elects a committee consisting of the president, vice president, secretary, joint secretary, treasurer and members. The number of members varies from college to college.
But, it’s no more the Panchayat system. Why do they exist today?

Student leaders say that FSU is the key medium to fight for the rights of students. According to them, the absence of FSU at the colleges recently has troubled the students and their education. Similarly, they also claim that the activeness of FSU compels the college administration to maintain transparency and pressure them on the academic and infrastructure development of the college.
However, there are questions if the FSU is still relevant given the student unions have focused their activities on political agenda, not academic ones. Hence, many consider such unions useless and unproductive. They are often blamed for creating an unhealthy environment at colleges. Most of the time they are involved in protests and fights rather than advocating for the students’ rights.
Perhaps that is why most of the privately run affiliated colleges do not hold the FSU elections whereas it has been a norm at constituent colleges run by the TU itself.
When do the elections happen?

The FSU elections are supposed to take place every two years. But due to political instability and disputes among student leaders and college administration, the FSU elections could not take place on time. The FSU elections, which are scheduled for March 19 are going to take place in full fledge after 14 years in the country the last full-fledged FSU elections took place in 2009 at all its constituents and affiliated colleges.
In 2017, the FSU elections were organised, but only 170 colleges participated in them. This time, however, the TU expects to hold the elections at all over 1,000 constituent and affiliated colleges.
Who can contest?
A candidate must be a student, not crossing the age of 28 years old. Likewise, the candidate must have one proposer and one seconder among the voters.
How do the elections happen?

The FSU elections follow a mixed electoral system as the House of Representatives elections. It means voting will be held under both first-past-the-post (FPTP) and proportional representation systems.
An 11-member committee will be elected at a college that has a maximum of 200 students. A 15-member committee will be elected if the number of students is between 201 and 1,000. Similarly, the committee will have 19 members if the college has 1,000 to 3,000 students. In case the number of students is more than 3,000, there will be 21 members on the committee.