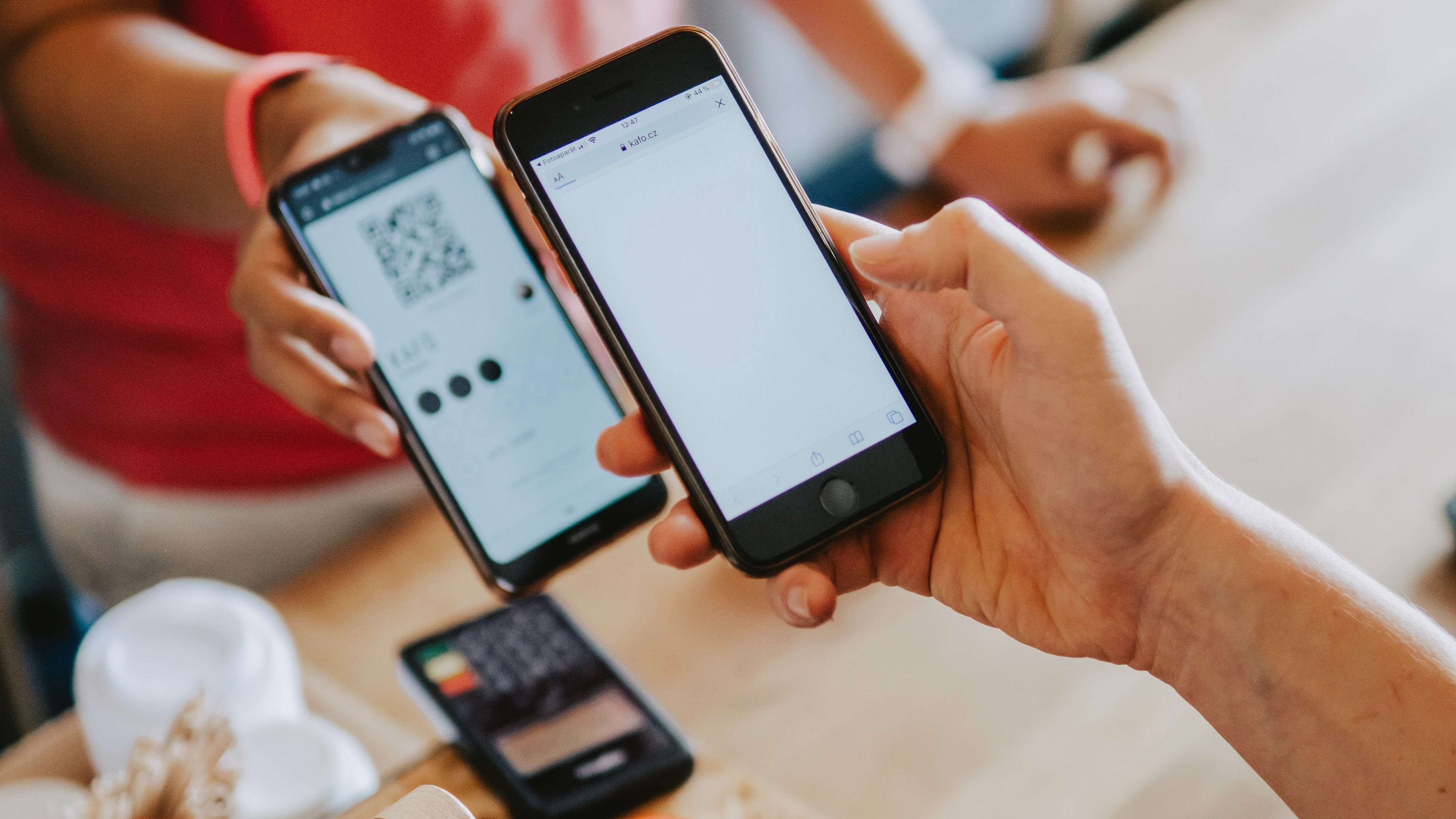
The progressive shift in banking from brick-and-mortar branches to the cashless modality has changed the way people access and avail financial services in Nepal. Online banking now affects the cash withdrawals from mobile wallets and digital payment systems every passing year in the financial industry of Nepal.
These compelling reasons come with the number of mobile phones penetrating the entire population, government initiatives toward financial inclusiveness, and their birth in the form of emerging Fintech companies.
New opportunities through technological advances in the banking sector accompany some really funny challenges blocking it, though. The article highlights how the digital banking scenario has evolved in Nepal, along with some probable advantages, mostly those hurdles still ahead of a secure and inclusive financial system.
Pushing more: Influences of Digital Banking in Nepal
The behavior of the consumers, techno-legal developments, and the rest would become factors favoring the growth of digital banking within Nepal. During 2024, approximately 13.5 million persons have entered the active world of social media in Nepal thus defining the size of the digital neighborhood for the country. The truth is that now mobile data services are way more affordable; hence, smartphone standardization has been happening fast and has spurred interest in personal digital finances.
Source: Different telecom providers including national statistics
DIGITAL TRANSACTION DEFINITELY FLEW OFF SKY HIGH given that Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB)reports over 20 million mobile banking customers in 2024. The birth of a national payment gateway, real-time transfer, and QR payment systems have revived the entire digital financial ecosystem in Nepal.
COVID would have pushed the wheel further. Incurred restrictions in movement accessed both businesses and customers to digital means for carrying out most financial activities. eSewa and Khalti were only two of many digital finance platforms that jumped into uncharted waters in user registration numbers like never before.
Opportunities presented by digital banking
1. Unlimited Access to Finance
Digital banking, quite understandably, has a point of selling owing to its increasing chances of access to finance, mostly in rural and remote areas; it is usually around or negligible from standard banking halls. The existence of bank branches such as that is always heavily costed concerning construction properties of bank buildings; on the other hand, mobile and internet banking brings the service literally to the hand of the ordinary user right on the cell phones. This mechanism thereby brings excluded communities within the economy into the network.
2. Making Economic Growth and Efficiency
Possible digital financial services are in a great position to play an important role in crafting the economy of Nepal, smoothing the transaction processes, and reducing operational costs while increasing efficiencies. Good digital banking platforms allow businesses to shrink payment cycles, be less cash-dependent, and improve operations; the somewhat cashless economy reduces inefficiencies arising from physical cash handling.
3. Supporting SMEs and Entrepreneurship
Digital banking has opened up new possibilities for SMEs-the backbone of the economy of Nepal. From online payments to applying for loans online and inter-branch remittances, these digital banking solutions connect even local businesses far and wide to reach an e-commerce-enabled market. In essence, they provide smaller and start-up businesses an unobstructed access bridge to digital credit and microfinance products, which are very enticing for an entity needing vital growth capital.
4. Fostering Innovation and Competition in Banking
Innovations brought by digital banking enhanced from a customer’s standpoint have created an entirely new competition amongst banks and other financial players, pushing them to innovate and upgrade their product offerings. Anything nimble and user-friendly like eSewa, Khalti, and IME Pay is forming an increasing threat to the traditional banking industry in terms of upgrading its digital offerings. This is beneficial to the client since they now have access to better services and lower transaction costs, as well as a better selection of choices.
Challenges facing digital banking in Nepal
With all the rush of digital banking, however, countless numbers of Nepalese become literate enough to have access to platforms that provide online financial services. Again, the rural areas are those where people are not yet aware of mobile banking apps and digital payment systems.
Misunderstandings and utterances against digital transactions cut short many savings users from feeling entirely comfortable. It is underdeveloped. Apart from that, internet performance, as far as metering systems are concerned, forms a big part of this value. It is still one wonderful deal for very high-altitude, far-away pockets all across the nation. However, on the other hand, Kathmandu, Pokhara, Birgunj and Biratnagar have high-speed internet access. In most rural areas, however, a lack of network coverage exists, and due to low internet capacity or un-affordability, digital banking remains hard by many.
1. Rising threats in cyber crime
Digital banking has become the army crawler that emerges with incredible need along with it in the line of cyber attacks. The goal is to decrease the level of phishing attacks, digital fraud, and unauthorized transactions in Nepal. Ignoring even the basic measures for cyber security makes this situation highly vulnerable to the online scourge. The absence of such a cyber security framework would create potential access routes for security incursions into financial institutions.
2. Regulatory policy gaps
The digitalization of banking is something that is changing so fast that there is a lag in rules keeping pace with such a speedy advancement of technology. Stronger policies on data protection, digital lending, as well as collaborations among Fintechs are instrumental in constituting a competitive environment. Consumer protection laws meant to protect the interest of digital banking users against fraud and service failure must also be strengthened.
3. Trust issues and resistance to change
Nepal is pretty much cash-centric in its character, with an overwhelming majority of older generations too failing to put their trust in electronic money transfers for fear that they would wrongly transact or be victims of cyber fraud. Many others perceive that their money might get lost due to technical failures or security breaches. In general, confidence among customers should be built by banks and Fintech companies by being transparent, having proper customer service, and sufficient regulatory oversight.
4. New developments and future projections
In addition, a government push for joint action with the private sector to surmount either of these hurdles could further support the establishment of a digital bank in Nepal. The Digital Nepal Framework of 2019 is aimed at ensuring that various digital solutions are deployed across sectors, including banking, in a multi-dimensional approach. Steps are continuing to ease the integration of mobile wallets.
Recent developments and their future prospects
It seems that an extremely high-level collaboration has begun between the private sector and Nepal’s government to eliminate some hindrances endured in the environment and to create a strong digital banking ecosystem in the nation. In 2019, a scheme was framed under the title Digital Nepal, to insert digital solutions into particular domains, banks being one of those sectors. Progress seems to have been made in the interoperability of mobile wallets and real-time settlement of payments, and investments, too, have seemed to yield good results in terms of cyber security.
Banks are trying to use AI and blockchain technology applications in their operations to secure banking processes and improve efficiency. AI chatbots, predictive analytics, and automated fraud detection systems are improving customer experience and risk mitigation in banks today.
Digitalizing banks is a very big step for Nepal towards modernization in finance since it is warranted. There is an urgent need to address digital illiteracy, threats to cyber security, and infrastructural inadequacies. The digital banking ecosystem should be in sync with the government and all other stakeholders in the financial sector, including traditional banks and Fintechs.
If feasible plans are made to utilize strategies for the digital banking platform, then Nepal can create a cost-effective and reliable financial ecosystem.