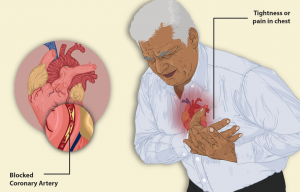
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading cause of death globally. According to the World Health Organization, ischaemic heart disease contributed to 16 per cent of the world’s total deaths, followed by stroke and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases in the second and third places.
In Nepal as well, CVDs are solely responsible for 26.9 per cent of the total deaths and 12.8 per cent of total disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Among the CVDs too, ischemic heart disease is contributing 16.4 per cent to total deaths and 75 per cent to total disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
CVD cases and deaths rose significantly from 1990 to 2017, and it is apparent that the cases are ever-rising. There are so many risk factors leading to CVDs. Lifestyle changes are also considered one of the leading causes. For developing countries such as Nepal, where people are fond of adapting to a modern lifestyle, this risk is even higher.
But, how does a modern lifestyle pose a threat to the human heart in Nepal?
Let’s discuss some of the elements of a modern lifestyle that may be contributing to heart problems in Nepal, on the occasion of World Heart Day 2021.
1. Use of tobacco

More than six million people die due to tobacco use every year, according to the World Health Organization. Further, it is projected that this number will increase to 10 million every year by 2030 if the current trend of tobacco use continues. The use of tobacco is the only preventable and leading cause of premature deaths from CVDs. As per a study, nicotine and carbon monoxide, among other components of tobacco smoke, also contribute to CVDs by affecting the myocardial (heart muscle) oxygen demand-supply balance.’
As per a 2020 review, over one-fifth population (21.6 per cent) of Nepal were tobacco users as of 2015. Most of them were men, under-educated, socioeconomically poor, and others. But, the consumption of tobacco is also increasing among youth and school students due to peer pressure and parental or family environment and as a part of the modern lifestyle, inviting a threat to CVDs and many more chronic diseases.
2. Alcohol consumption

Binge drinking, which refers to drinking more than five standard drinks at one time, is linked with a rise in blood pressure levels posing threat to human health. Also, binge drinking is also associated with increased odds of clinically high total serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels.’ About 23.9 per cent of adults, or 4.8 million (3.7 million men and the rest women), were current drinkers, referring to the people who consumed alcohol in the past 12 months, in 2019.
In Nepal, about 11.7 per cent drank daily and almost 6.8 per cent of adults engaged in heavy episodic drinking in 2019, according to Nepal STEPS Survey 2019 Alcohol Consumption and Policy Factsheet.
Like the use of tobacco, alcohol consumption has become a huge part of the modern lifestyle in Nepal as it is also a part of the Nepali tradition for many people. And, with each passing day, many young, as well as older people, are getting into it, increasing the risk of CVDs.
3. Unhealthy diet

Many Nepali people, especially in urban areas, are usually consuming a diet low in whole grains, and low in fruits. They are usually feeding on junk and fast food due to various reasons.
When one consumes such a diet which is high in saturated and trans fats, excessive sugar, and salt, it will ‘cause cholesterol to build up in your blood vessels (arteries.)’ Not only that, an unhealthy or poor diet can lead to obesity and increased blood pressure levels, all eventually contributing to CVDs.
And, this will put you at risk for several heart diseases including heart attacks.
4. Insufficient physical activity

A sedentary lifestyle with insufficient physical activity is the prime cause of the proliferation of many CVDs in many people in Nepal as well as in other parts of the world. A sedentary lifestyle can cause obesity, hypertension, and much more, all posing a fatal threat to human health.
And, with the advent of a lot of facilities such as transportation and mobile phones, many people have opted for a sedentary lifestyle, particularly in cities, putting themselves at risk of heart diseases and much more.
5. Irregular sleep

In a study conducted among 1,992 men and women of age group 45-84 who initially did not have any CVDs, for five years, it was found that ‘irregular sleep patterns double the risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults.’
With many people adopting the modern lifestyle in Nepal, there has been a drastic change in their sleep patterns of people. Most people tend to use mobile phones, particularly using social media platforms till late at night, and hence wake up very late in the morning. This tendency is very likely to increase the risk of CVDs.
6. Multitasking and overworking

Multitasking and overworking have become the common practice of people living the modern lifestyle, without knowing what this practice could lead to.
Spending a lot of hours at work has an immediate impact on cardiovascular diseases as it adds up to stress levels. According to a study, work-related stress is likely to double the risk of coronary heart disease.
Originally published on September 29, 2021